Master AI Finance Automation with Agentic Systems

Drowning in manual tasks, legacy systems, and slow-moving processes? You're not alone, and you are not stuck AI finance automation is changing the game. Here's how to catch up, and get ahead.
For years, finance teams have battled a persistent tension: balancing precision and compliance with speed and scalability. While other departments flirted with agile tools and sleek digital workflows, many finance and accounting functions remained tethered to manual tasks, brittle spreadsheets, and software systems designed in a different era.
Why? Because finance is different. The stakes are higher, the regulations are stricter, and the workflows are more entangled. You can’t automate journal entries or revenue recognition using the same logic applied to scheduling social media posts.
That’s exactly what makes automation in finance a necessity today, not a nice-to-have.
Finance leaders are facing increasing pressure to close the books more quickly, maintain thorough audit trails, identify risk factors early, and support real-time decision-making. Legacy tools using robotic process automation (RPA) offered some relief, but their rule-based structure lacks adaptability. These systems can't reason through exceptions or learn from evolving financial workflows. They were never designed for the level of complexity modern financial operations now demand.
Now, a new class of intelligent systems is changing the game. Agentic AI brings decision-making capability to automation. These AI agents don’t just follow instructions! They interpret context, adapt in real time, and carry out financial tasks across fragmented systems without constant human input. It’s a shift from task automation to outcome automation.
This article AI finance automation has evolved, why this shift matters now, and how no-code platforms like Capably make it more accessible. Whether you're just starting to modernise or aiming to future-proof your financial operations, this guide will help you understand what's possible, and how to get there.
What Is Automation in Finance? A Brief Primer
Automation in finance refers to the use of technology to perform routine, rules-based, or repetitive tasks without manual input. It has long been a core strategy for increasing efficiency, reducing human error, and enabling finance teams to focus on more strategic work. But not all automation is created equal.
At its most basic, automation might mean a spreadsheet macro that populates monthly reports. More advanced versions, like robotic process automation, mimic human actions by clicking through interfaces and moving data between systems. RPA is still widely used, but it struggles when workflows involve variability, unstructured data, or constant change, which describes many real-world financial operations.
For example, automating invoice processing with RPA works until a vendor submits a slightly different format, or a field doesn’t match the expected pattern. Then, a person must step in, and the automation stalls. This is where traditional tools hit a ceiling.
Modern AI tools move beyond mimicking clicks. With technologies like machine learning, natural language processing, and intelligent data parsing, they can interpret context, learn from patterns, and adjust as conditions evolve. This opens the door to automating not just individual tasks, but entire financial workflows.
As we’ll explore in the next section, the latest evolution—agentic process automation (APA)—combines these capabilities with autonomous decision-making. It’s not just about speeding up processes. It’s about building a smarter, more adaptable finance function that can operate in real time, across fragmented systems, without hand-holding.
Why Now? Agentic AI and Accessibility
The finance world isn’t exactly known for jumping on every new tech trend, and for good reason. Accuracy, compliance, and risk mitigation tend to outrank novelty. But something has shifted. Traditional automation is no longer enough, and finance teams are feeling the cracks.
Robotic process automation (RPA) helped many organisations speed up tasks like invoice approvals and reconciliations. But these systems were designed to follow strict rules, not to think or adapt. They break easily when formats change, systems update, or exceptions arise. And as financial processes become more complex and interconnected, the limitations of rigid automation become painfully clear.
At the same time, advances in AI are unlocking a new paradigm: Agentic Process Automation (APA). APA refers to the use of AI “agents” that don't just automate tasks—they reason, adapt, and pursue outcomes. Unlike rule-bound systems such as RPA, which follow predefined scripts, agentic AI agents can interpret context, make decisions based on real-time data, and recover from unexpected input without human intervention.
What makes an AI system agentic is its ability to:
- Operate autonomously toward a goal (not just follow static instructions);
- Perceive and respond to dynamic environments (e.g., changing data formats, policies, or exceptions);
- Learn and adapt behaviour over time;
- Coordinate across multiple systems and workflows.
Architecturally, these agents often combine components like large language models (LLMs), workflow orchestrators, memory layers, and context-aware decision engines. This allows them to reason through ambiguity, initiate actions, and interact with humans and machines without rigid programming.
Where traditional automation focuses on task execution, APA is about outcome achievement—unlocking scalable, adaptive workflows in finance without constant oversight. For example, an AI agent can learn vendor invoice patterns, flag invoice exceptions, map data to account codes, initiate necessary approvals, and maintain a full audit trail. This marks a clear departure from brittle, rules-based automation.
Why jump on the opportunity now?
One recent study indicates a massive gap. According to McKinsey's 2024 survey, 98% of CFOs claimed they are investing in digitisation and automation. However, almost half also said that only 25% of processes are automated. These numbers reveal enormous untapped potential for smarter finance automation.
It's an opportunity, but one that won't last forever. Another 2024 projection by KMPG indicates that the current 38% of finance leaders investing in AI will grow to 95% in 3 years. Add to that the rising budgets for AI and automation. For example, a Morgan Stanley report found that financial services firms increased their AI adoption from 66% to 73% in just a few months during early 2025. The shift toward intelligent systems is clearly gaining momentum. For finance leaders, waiting too long to automate could mean falling behind the competition.
The convergence of stronger AI tools at scale and accessible low-code deployment platforms has made APA achievable right now. Finance teams no longer need brittle, rule-bound systems. They can automate dynamic workflows that evolve with the business—without coding or IT-heavy implementations.
What are the Benefits of AI Automation in Financial Services?
Finance leaders are acutely familiar with these challenges: teams swamped by manual tasks, long close cycles, rising error rates, and limited capacity for strategic insight. These pressures compound risk, slow decision-making, and drain resources. AI automation promises to resolve many of these pain points—and here’s how it delivers real, measurable value.
1. Operational Efficiency and Speed
When finance teams rely on manual data gathering and task execution, every close cycle suffers delays. Observing automation in financial reporting across a variety of companies shows that smart technologies enhance reporting consistency and minimise errors, boosting credibility and accelerating close times. Furthermore, McKinsey's study shows that up to 57% of finance tasks—particularly transactional and rules-based activities—can be fully or mostly automated using current technologies. This automation potential significantly reduces processing times and allows finance teams to shift focus toward higher-value, strategic work.
2. Accuracy, Compliance, and Fraud Detection
Manual journal entries, invoice matching, and financial reporting are susceptible to human error. Automated systems reduce error rates and ensure data integrity. Trintech notes that automation leads to more consistent and accurate financial reporting.
Academic studies reinforce that artificial intelligence and machine learning significantly improve fraud detection and control, enhancing both accuracy and regulatory compliance. A systematic review of 93 peer-reviewed articles found that models such as support vector machines and neural networks consistently outperformed traditional methods in analysing financial data for anomalies. Another study showed a hybrid deep learning system achieved 98.7% accuracy, 94.3% precision, and 91.5% recall, while supporting AML and KYC requirements.
3. Strategic Insight and Forecasting
Traditional workflows leave little room for predictive analytics or real-time forecasting. Automation unlocks both. One report shows organisations improve forecast accuracy by 37 % and reduce planning cycle time by 70 % when implementing automated workflows. With accurate forecasts and scenario planning, finance can guide the business forward instead of reporting the past.
4. Scalability and Adaptability
As your organisation scales or financial systems evolve, rigid automation breaks. Modern AI agents adjust to changes without constant manual updates. Case studies demonstrate up to 80 % reduction in processing time for expense tasks using generative AI and intelligent document processing combined with smart agents—and much lower error rates in complex workflows.
5. Empowering Teams and Eliminating Manual Tasks
Finance teams often carry outdated, manual workloads that hinder strategic progress. A Gartner study found that RPA can eliminate up to 25,000 hours of avoidable rework annually within finance departments—equivalent to roughly 30% of each employee’s time spent on repetitive tasks. That's just RPA! Now imagine you up the game with autonomous AI.
As automation replaces these tedious duties, teams report higher engagement and lower turnover, shifting their focus toward more impactful work such as analysis, forecasting, and strategic planning.
Together, these benefits make an undeniable case: AI finance automation moves finance from being reactive to becoming proactive and strategic. It addresses core pain points—speed, accuracy, compliance, capacity—and creates a foundation for modern finance transformation.
Real-World Use Cases: What Can Be Automated?
For finance leaders, the pressure isn’t just to automate, it’s to do so in ways that deliver measurable ROI. Budgets are under scrutiny, expectations are high, and teams are already stretched thin. The most effective approach is to focus on high-impact financial tasks where automation has already proven to be effective, scalable, and safe.
From accelerating close cycles to improving compliance and boosting liquidity, agentic AI finance automation is now being applied to dozens of common workflows. These aren’t future-state experiments. They’re happening now, in finance departments across industries, and often without a single line of code.
✅ Invoice Processing and AP Automation
From invoice data capture to invoice matching and approvals, AI tools can handle thousands of invoices each day without requiring manual review. Using machine learning algorithms and natural language processing, these tools extract line items, classify account codes, and match invoices against POs or contracts.
Automating these steps reduces human error and accelerates accounts payable (AP) cycles. A Capgemini study found that companies using autonomous AI automation in AP reduced late supplier payments by 81% and cut invoice processing costs by 67%.
🔄 Journal Entries and Month-End Close
Manual journal entries can delay the close and introduce risk. By automating recurring entries and suggesting variable ones, AI helps finance teams reduce bottlenecks during peak close periods. AI assistants can surface anomalies, match entries to supporting data, and reconcile discrepancies as they arise.
This approach enables real-time schedules for closing the books and shifts the focus from manual preparation to strategic oversight.
🔍 Expense Audits and Compliance Monitoring
Expense reports are a common source of policy violations and fraud. Agentic workflows can automate the expense audit process by flagging duplicate submissions, identifying high-risk categories, and cross-referencing spending patterns against company policy.
This reduces manual tasks and increases audit readiness, especially when integrated with controls for regulatory compliance and expense controls. With continuous learning, these systems become more accurate over time.
💸 Accounts Receivable and Cashflow Forecasting
Smart automation workflows can accelerate collections by analysing customer behaviour, predicting late payments, and generating personalised follow-ups. Combined with predictive analytics, these tools help finance teams proactively manage cash flow and reduce days sales outstanding (DSO).
Intelligent AI agents prioritise outreach and identify accounts that need escalation before they become a problem.
📊 Financial Reporting and Controls
Preparing reports for management, audits, and regulators demands accuracy and traceability. AI can help gather and normalise data from ERP systems, populate reporting templates, and provide a full audit trail to support transparency.
Some systems also apply generative AI to produce draft narratives or board-ready summaries, which helps FP&A teams cut down reporting time significantly.
📂 Contract Extraction and Revenue Recognition
Financial data often lives in contracts stored across emails and PDFs. With the help of AI models trained on legal and accounting terminology, finance teams can extract billing schedules, service terms, and performance obligations.
This is especially useful for automating revenue recognition under standards like ASC 606 or IFRS 15, where precision and compliance are non-negotiable.
| Use Case | Impact | Enabling Tech |
|---|---|---|
Invoice Processing | Faster payments, fewer invoice exceptions, lower cost | Agentic automation with NLP and machine learning |
Journal Entries & Close | Faster close, fewer errors, less pressure | Agentic automation with anomaly detection |
Expense Audit | Compliance, fraud detection, and time savings | Agentic automation with policy logic and AI models |
Accounts Receivable | Shorter DSO, better collections | Agentic automation with predictive analytics |
Financial Reporting | Accuracy, visibility, and full audit trail | Agentic automation integrated with ERP systems |
Contract Extraction | Faster recognition, global compliance support | Agentic automation with NLP and generative AI |
By focusing on use cases where automation has already shown measurable value, finance leaders can target the highest-return opportunities. With agentic process automation (APA) and modern platforms, it’s now possible to automate workflows that once required judgment, memory, or domain expertise.
What are the Challenges and Ethical Considerations?
Automation promises big gains, but it’s not without its hurdles. Finance leaders must navigate risks related to technology, data, compliance, and trust. Understanding these challenges upfront helps ensure successful, responsible adoption of agentic AI in finance automation.
Data Quality and Integration
AI models rely heavily on clean, consistent data. Unfortunately, financial systems are often fragmented, with legacy software and siloed databases creating messy inputs. Without good data gathering and integration, even the smartest AI agents can produce flawed outputs.
Finance teams need to prioritise data hygiene and connect automation to their core ERP systems and financial platforms. A robust foundation avoids costly errors down the line and supports regulatory demands.
Balancing Automation and Human Oversight
Despite AI’s sophistication, human oversight remains essential. Agentic automation can handle complex workflows, but unexpected scenarios still arise. Finance professionals must monitor outputs and intervene when models behave unpredictably.
This hybrid approach preserves control and accountability. It also helps manage risk factors inherent to automated decisions, especially around sensitive areas like fraud detection and regulatory compliance.
Ethical Use and Bias Mitigation
AI systems reflect the data they are trained on. In finance, biased historical data can inadvertently lead to unfair decisions or missed risks. It’s critical to build, test, and regularly audit AI models to detect and correct bias.
Transparency is key. Clear explanations of how AI reaches decisions build trust with auditors, regulators, and internal stakeholders. Many firms are adopting ethical AI frameworks aligned with industry standards to guide development and deployment.
Regulatory Compliance and Security
Financial services are highly regulated, with strict rules on data privacy, reporting, and audit trails. Automation must ensure full compliance with frameworks like GDPR, SOX, and global tax laws.
Security is also paramount. AI systems must safeguard sensitive financial data against breaches. This requires encrypted data flows, strong access controls, and regular vulnerability assessments.
Change Management and Workforce Impact
Adopting agentic process automation involves cultural change. Teams may worry about job security or struggle to trust AI outputs. Finance leaders should invest in clear communication, training, and involving staff early in the process.
Rather than replacing people, AI enables finance professionals to focus on higher-value work, while automating repetitive manual tasks.
By addressing these challenges thoughtfully, finance organisations can unlock the full potential of agentic process automation while maintaining ethical, secure, and compliant operations.
How to Automate Finance: Without Code or Complexity
Until recently, automating finance workflows often meant long IT timelines, heavy systems integration, and the kind of complexity that discouraged even the most forward-thinking finance teams. But that’s no longer the case.
The shift toward agentic AI isn’t just about smarter automation; it’s about accessibility. Today’s autonomous AI platforms, like Capably, remove the traditional barriers. There’s no need to code, no dependency on overburdened IT teams, and no steep learning curve. This puts finance professionals, not engineers, at the helm of automation.
Capably stands out because it’s purpose-built for agentic process automation in finance and other departments. It comes with an AI Capability Library of pre-built workflows designed around real-world processes such as invoice matching, journal entries, and expense audits.
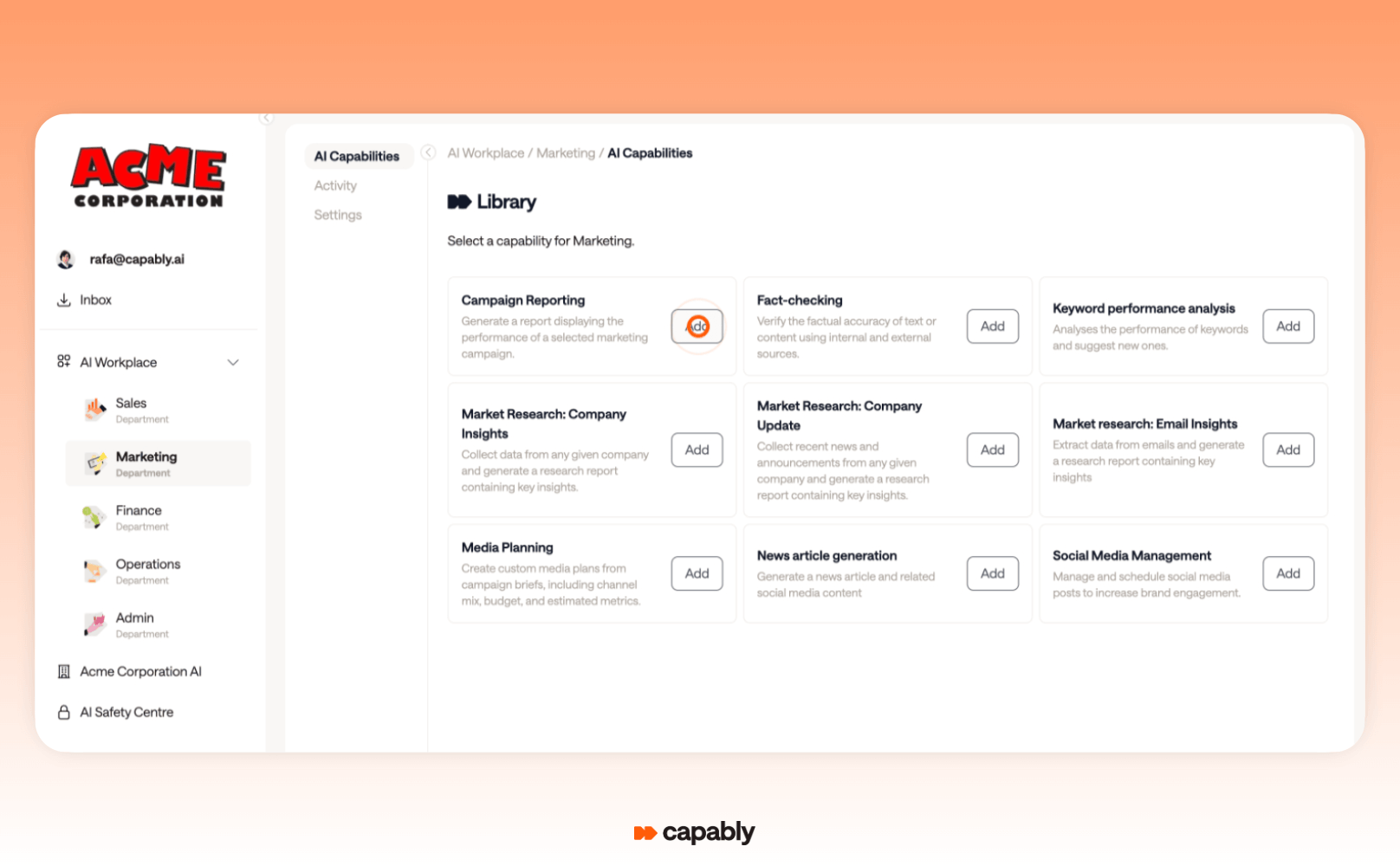
These templates aren’t generic. They’re intelligent, adaptive workflows that can be used as-is or customised to suit your specific requirements.
For teams with unique processes, Capably’s guided, no-code approach makes it easy to build something new from scratch.
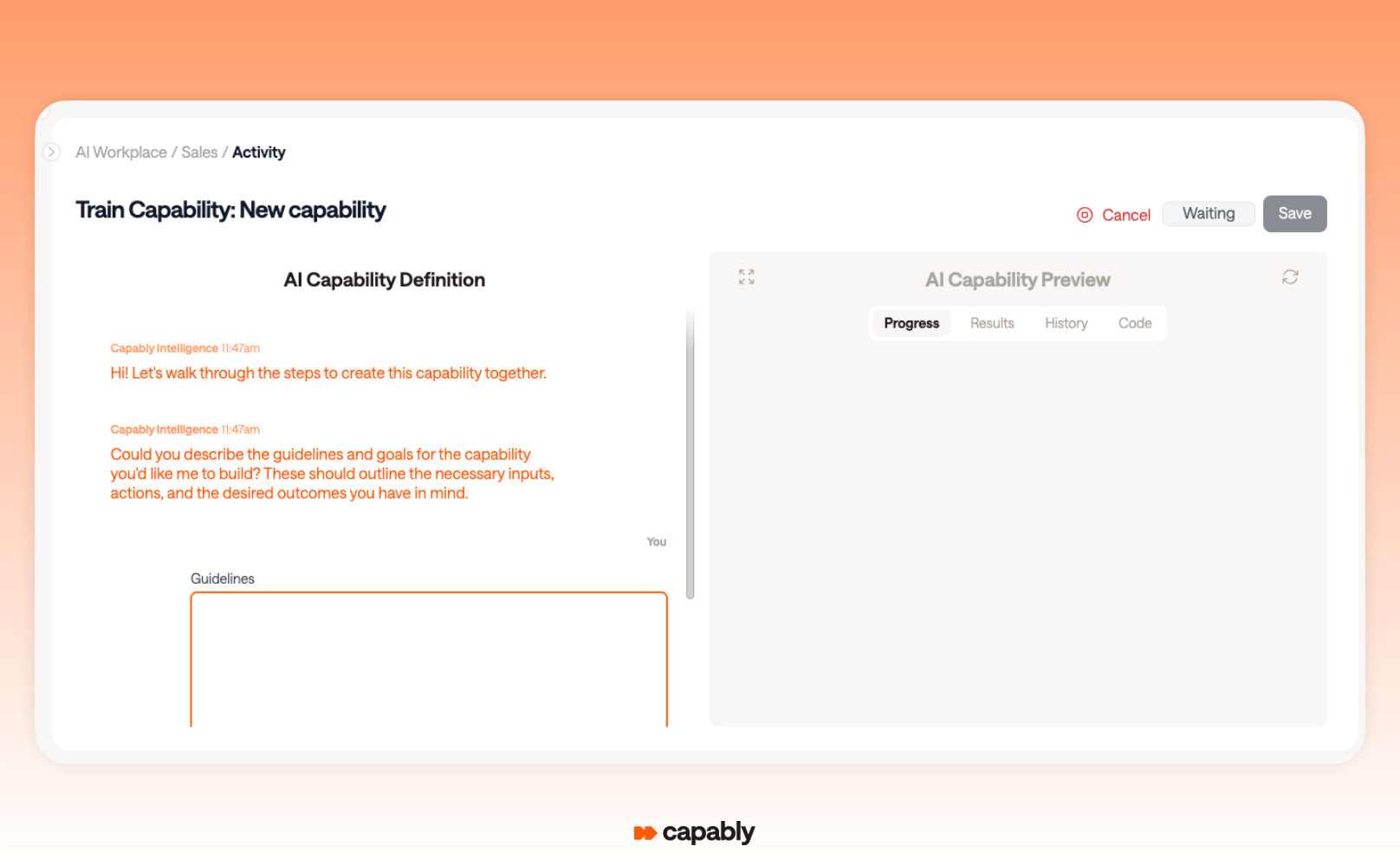
It uses a collaborative flow: you describe what you want to automate, the system responds with what it needs to make that happen, and together you test, refine, and launch. The final result can be saved to your own workflow library and scaled across teams.
That’s the real value here: Speed, simplicity, and control.
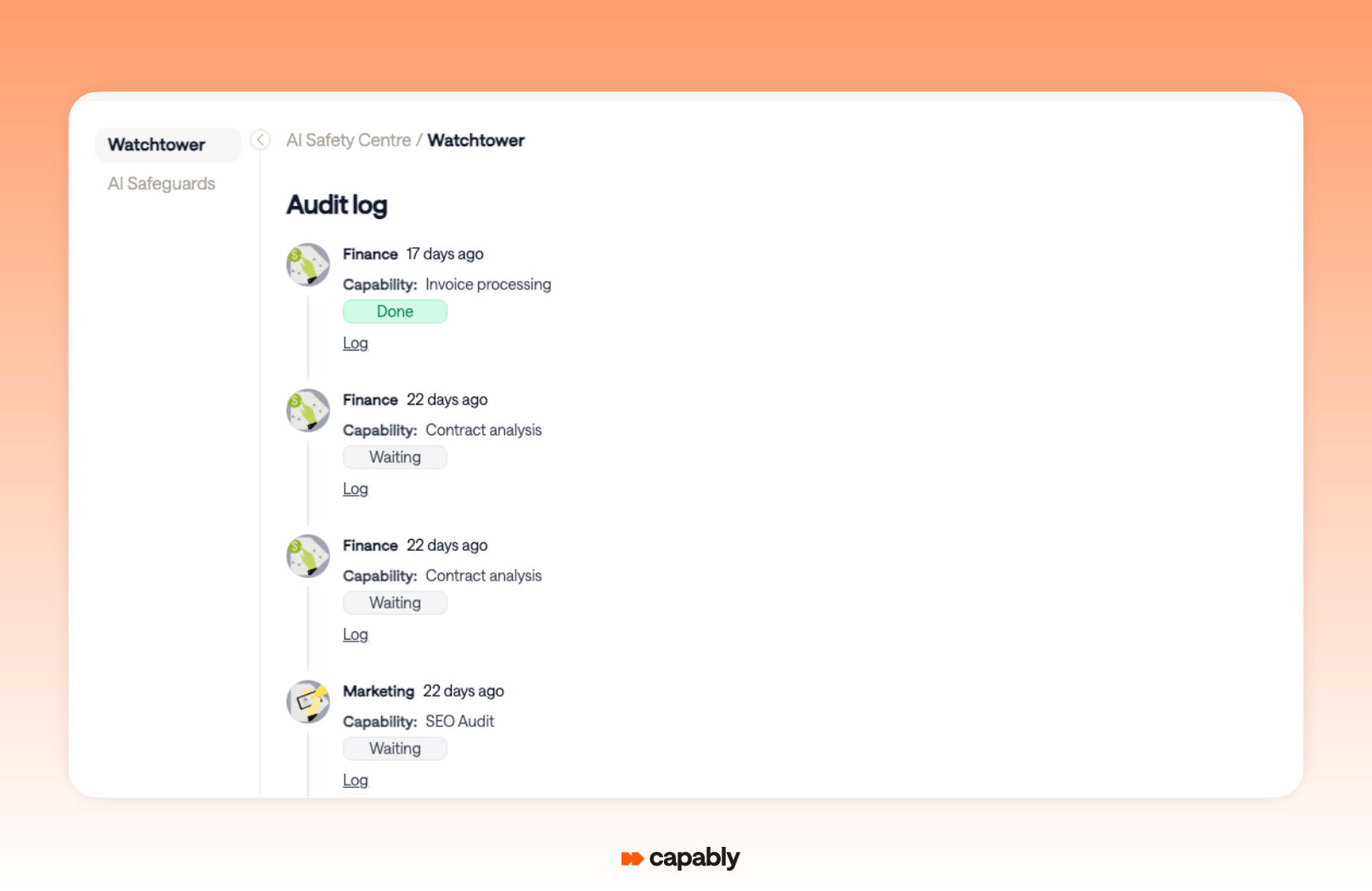
Capably allows finance teams to move fast without compromising on governance or security. Built-in compliance features, policy checks, and data-access controls support both audit readiness and global regulatory standards.
There’s a full audit trail, so every action is traceable, and exception handling is baked in from the start.
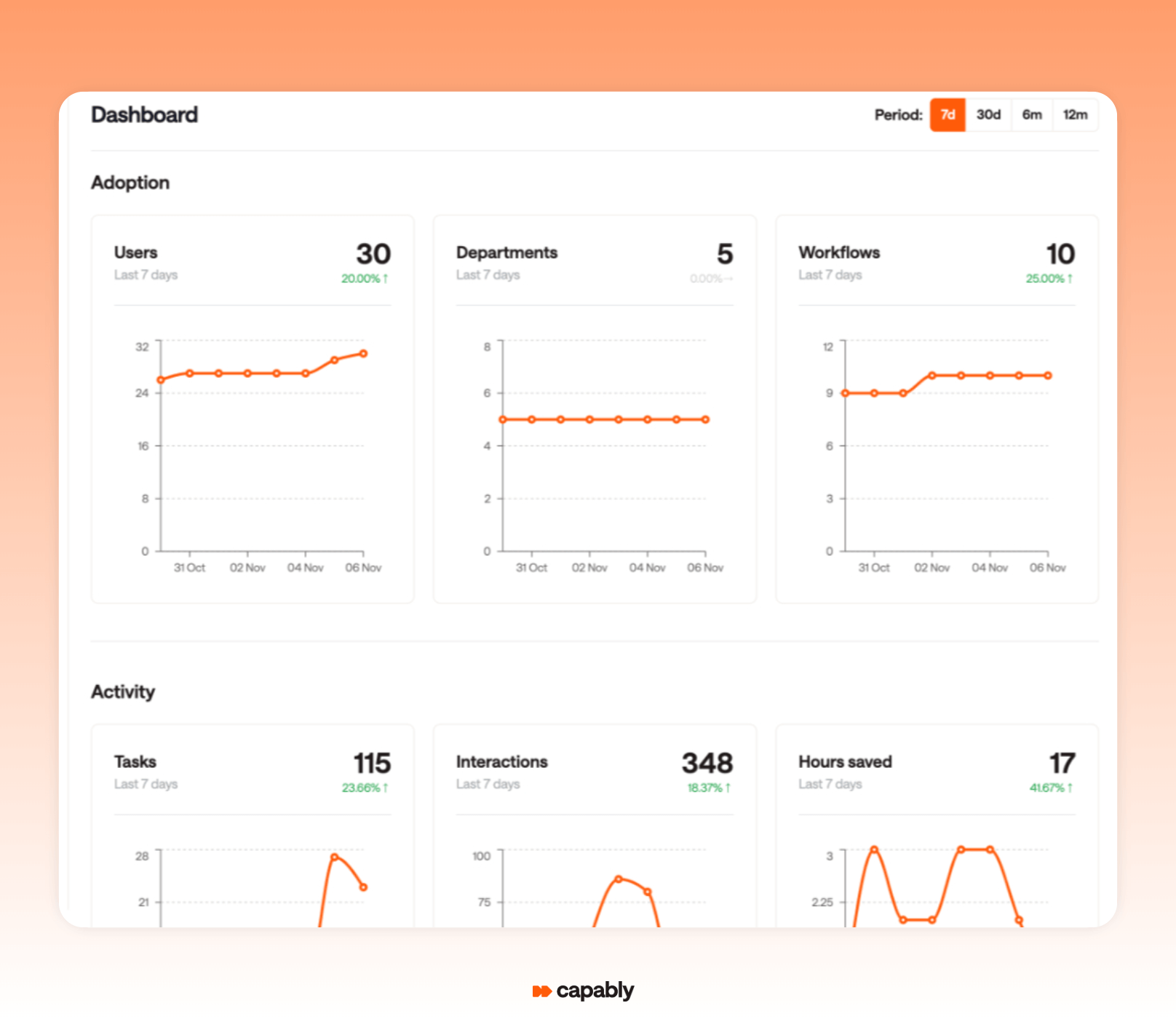
Transparency also isn’t an afterthought. The platform gives teams insight into workflow activity, usage frequency, and performance, so you can track adoption and effectiveness in real time.
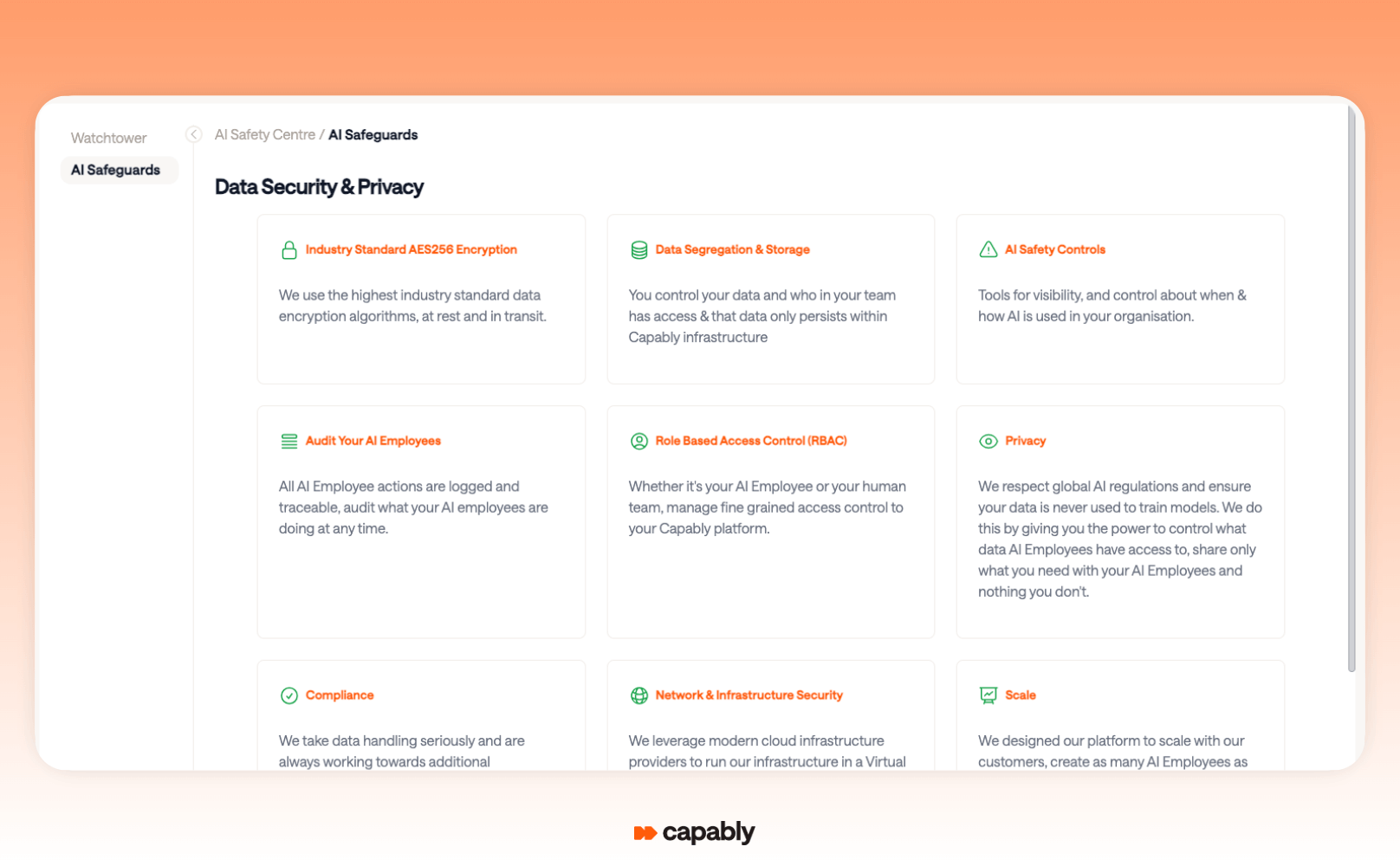
It’s this level of visibility that helps finance leaders not only launch automation, but manage and optimise it over time.
In short, the reason AI finance automation is becoming more mainstream isn’t just because the technology has evolved. It’s because platforms like Capably have made it manageable, measurable, and (critically) available to the people who know finance best.
Conclusion: The Future Is Autonomous, and It’s Here
Smart finance automation is overdue. Manual approvals, disconnected systems, and spreadsheet sprawl no longer belong in an era where AI agents can reason, adapt, and execute at speed.
With the rise of agentic process automation and no-code platforms like Capably, your finance team doesn’t have to wait for IT, learn to code, or settle for brittle RPA scripts. You can build smarter workflows that evolve with the business, reduce risk, and elevate decision-making.
The tools are ready. The use cases are proven. The competitive advantage is real.
Now it’s just a question of who moves first, and who’s left playing catch-up.
FAQs
How long does it typically take to implement Capably for finance automation?
Implementation timelines vary by organisation size and complexity, but many finance teams begin automating with Capably in a matter of days/weeks. Thanks to pre-built workflows and a no-code interface, initial setup and pilot projects can be completed quickly, often within a few weeks.
Does Capably require IT involvement for ongoing workflow management?
No. Capably is designed so that finance professionals can create, test, and modify workflows independently. This reduces the typical IT bottleneck and empowers finance teams to adapt automation as business needs evolve.
How does Capably ensure data security and regulatory compliance?
Capably integrates with existing ERP systems and includes robust security measures like role-based access, encrypted data handling, and detailed audit logs. Its compliance features align with standards such as SOX, GDPR, and industry-specific regulations, helping firms maintain governance without extra overhead.
Can Capably integrate with existing financial systems and tools?
Yes. Capably supports seamless integration with common ERP platforms, accounting software, and data sources to unify workflows. This interoperability ensures that automation works with your existing infrastructure rather than replacing it.
What support is available during and after implementation?
Capably offers dedicated onboarding assistance, helping your team set up workflows and tailor automation to your processes. Post-implementation, ongoing support and resources ensure continuous improvement and scalability.